
Reserch
Institute for Molecular and Cellular Regulation
Laboratory of Molecular Cell Biology

Fuminori Tokunaga professor
NF-κB pathway is a pivotal signal transduction pathway for innate and acquired immune regulation, inflammatory responses, and apoptosis. Dysregulation of NF-κB signaling cause multiple disorders, such as cancers, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, metabolic syndrome, and neurodegenerative disorders. NF-κB activation pathway is regulated by various post-translational modifications including phosphorylation and ubiquitination. We are currently investigating the pathophysiological functions of (1) linear ubiquitination-mediated NF-κB regulation and (2) apoptosis-regulating kinases, in order to identify novel drug targets for cancers, chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, and diabetes.
Research
1. Linear ubiquitination-mediated NF-κB regulation
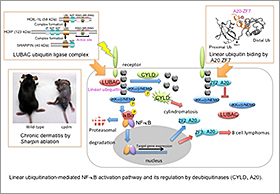
We identified LUBAC ubiquitin ligase complex, which generates a novel type of Met1-linked linear polyu biquitin chain, and regulates canonical NF-κB pathway. LUBAC is composed of HOIL-1L, HOIP, and SHARPIN. Genetic ablation of LUBAC components induces inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. Moreover, we identified that deubiquitinase A20 suppresses LUBAC-mediated NF-κB activation by the specific binding to linear ubiquitin chain at zinc finger (ZF) 7 domain. Genetic mutations which cause loss of the intact A20 ZF7 possibly induce B cell lymphomas. Further pathophysiological functions of linear ubiquitination are under investigation.
2. Apoptosis regulation by phosphorylation-dependent signals
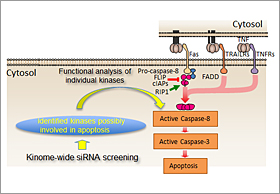
Deregulation of programmed cell death such as apoptosis contributes to the pathogenesis of various diseases. However, signaling pathways leading to cell death are still incompletely defined. In a kinome-wide siRNA screening, we identified kinases related to apoptosis mediated by death receptors such as TNFR, Fas or TRAILRs. Our interest is to clarify the functions of these kinases, and to elucidate the precise mechanisms of apoptosis induction. We also focus on the role of these kinases in alternative cell death machinery such as necroptosis.
Recent Publications
- Kato K., Ishii R., Goto E., Ishitani R., Tokunaga F., and Nureki O. Structural and functional analyses of DNA-sensing and immune activation by human cGAS. PLoS One, 8 (10), e76983, (2013)
- Tokunaga F. Linear ubiquitination-mediated NF-κB regulation and its related disorders. J. Biochem., 154 (4), 313-323, (2013)
- Naguro I., Umeda T., Kobayasi Y., Maruyama J., Hattori K., Shimizu Y., Kataoka K., Kim-Mitsuyama S., Uchida S., Vandewalle A., Noguchi T., Nishitoh H., Matsuzawa A., Takeda K., and Ichijo H. ASK3 responds to osmotic stress and regulates blood pressure by suppressing WNK1-SPAK/OSR1 signaling in the kidney. Nat. Commun., 3, 1285, (2012)
- Tokunaga F., Nishimasu H., Ishitani R., Goto E., Noguchi T., Mio K., Kamei K., Ma A., Iwai K., and Nureki O. Specific recognition of linear polyubiquitin by A20 zinc finger 7 is involved in NF-κB regulation. EMBO J., 31 (19), 3856-3870, (2012)
- Yagi H., Ishimoto K., Hiromoto T., Fujita H., Mizushima T., Uekusa Y., Yagi-Utsumi M., Kurimoto E., Noda M., Uchiyama S., Tokunaga F., Iwai K., and Kato K. Non-canonical UBA–UBL interaction mediates formation of linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex. EMBO Rep., 13 (5), 462-468, (2012)
- Kensche T., Tokunaga F., Ikeda F., Goto E., Iwai K., and Dikic I. Analysis of NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO) binding to linear and lysine-linked ubiquitin chains and its role in the activation of NF-κB. J. Biol. Chem., 287 (28), 23626-23634, (2012)
- Tokunaga F., Nakagawa T., Nakahara M., Saeki Y., Taniguchi M., Sakata S., Tanaka K., Nakano H., and Iwai K. SHARPIN is a component of the NF-κB activating linear ubiquitin assembly complex. Nature, 471 (7340), 633-636, (2011)
- Ikeda F., Deribe Y.L., Skånland S.S., Stieglitz B., Grabbe C., van WijK S., Franz-Wachtel M., Goswami P., Nagy V., Terzic J., Tokunaga F., Androulidaki A., Nakagawa T., Pasparakis M., Iwai K., Sundberg J.P., Schaefer L., Macek B., Rittinger K., and Dikic I. SHARPIN forms a linear ubiquitin ligase complex regulating NF-κB activity and apoptosis. Nature, 471 (7340), 637-641, (2011)
- Inn K.S., Gack M.U., Tokunaga F., Shi M., Wong L.Y., Iwai K., and Jung J.U. Linear ubiquitin assembly complex negatively regulates RIG-I- and TRIM25-mediated type I interferon induction. Mol. Cell, 41 (3), 354-365, (2011)
- Tokunaga F., Sakata S., Saeki Y., Satomi Y., Kirisako T., Kamei K., Nakagawa T., Kato M., Murata S., Yamaoka S., Yamamoto M., Akira S., Takao T., Tanaka K., and Iwai K. Involvement of linear polyubiquitylation of NEMO in NF-κB activation. Nat. Cell Biol., 11 (2), 123-132, (2009)
Members

Professor: Fuminori Tokunaga
Assistant Professor: Takuya Noguchi
Assistant Professor: Eiji Goto
Research
Assistant Professor: Daisuke Oikawa
Graduate Student: Seshiru Nakazawa
Medical Student: Takuya Kumazawa
Research Technician: Kiyoko Kamei
Assistant Technician: Keiko Kawajiri
TEL: +81-27-220-8865
FAX: +81-27-220-8897
E-mail: ftokunaga@gunma-u.ac.jp
HP: http://molcellbiol.imcr.gunma-u.ac.jp/ ![]()
