
Reserch
Institute for Molecular and Cellular Regulation
Laboratory of Cell Physiology
Itaru Kojima Professor
Specific aims
Elucidation of (1) actions and mechanism of actions of hormones, growth factors and cytokines involved in metabolic regulation, tissue repair and regeneration, and (2) their physiological and pathophysiological roles in relation to diabetes, obesity, cancer and tissue fibrosis.
On-going projects
1. Action and mechanism of actions of hormones, growth factors and differentiation factors
We are investigating the actions and mechanism of actions of various hormones, growth factors and differentiation factors. We are also studying the physiological and pathophysiological roles of these factors in metabolic disorders and tissue fibrosis.
(1) Function of the sweet taste-sensing receptor:
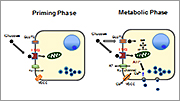
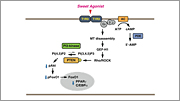
Sweet taste receptor expressed in the taste bud is a heterodimmer of T1R2 and T1R3. It is also expressed in enteroendocrine cells, pancreatic ß-cells and adipocytes. In these cells, a homodimer of T1R3 may act as a sweet taste-sensing receptor. We are now investigating the function of the sweet taste-sensing receptor in these cells. In particular, this receptor functions as a glucose-sensing receptor in pancreatic ß-cells. We are now studying the role of this receptor in glucose-induced insulin secretion.
(2) Regulation of tissue regeneration and fibrosis:
We have been studying the growth factors and differentiation factors involved in regeneration of pancreatic ß-cells. We are now trying to establish a method to promote ß-cell regeneration using these factors. We are also studying the factors regulating fibrosis of the pancreas, liver and lung. Using a compound conophylline, we are now trying to establish a method to prevent tissue fibrosis.
(3) Calcium-permeable channel TRPV2:
We have been studying the regulation of calcium-permeable cation channel TRPV2. We are particularly interested in the trafficking of TRPV2 and physiological role of trafficking of TRPV2.
2. Mechanism of action of insulin on glucose transport
Insulin promotes glucose transport in adipocytes and myocytes. To this end, insulin induces translocation of a glucose transporter GLUT4 from an intracellular storage pool to the plasma membrane. We have been studying the trafficking of GLUT4 in adipocytes. Currently, we are studying the mechanism of insulin-induced down-regulation of GLUT4 in adipocytes.
 |
 |
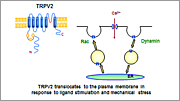 |
| A New Model for the Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion | Signal Transduction Pathway Activated by the Sweet Taste-sensing Receptor in Adipocytes | Translocation of TRPV2 |
Recent Publications
- Kubo N, Saito R, Hamano K, Nagasawa M, Aoki F, Takei I, Umezawa K, Kuwano H, Kojima I.: Conophylline suppresses hepatic stellate cells and attenuates thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats. Liver Int (in press)
- Nakagawa Y, Ohtsu Y, Nagasawa M, Shibata H, Kojima I.: Glucose promotes its own metabolism by acting on the cell-suface glucose-sensing receptor T1R3. Endocrine J (in press)
- Masubuchi Y, Nakagawa Y, Ma J, Sasaki S, Kitamura T, Yamamoto Y, Kurose H, Kojima K, Shibata H.: Novel regulatory function of sweet taste-sensing receptor in adipogenic differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells. PLoS ONE 8: e54500 (2013)
- Yoshida R, Yamada S, Hara A, Yamamoto Y, Kodera T, Tanaka Y, Kimura F, Takei I, Umezawa K, Kojima I.: Conophylline suppresses pancreatic stellate cells and improves islet fibrosis in Goto-Kakizaki rats. Endocrinology 153: 621-630 (2012)
- Nagasawa M, Kojima I.: Translocation of calcium-permeable TRPV2 channel to the podosome: its role in the regulation of podosome assembly. Cell Calcium 51: 186-193 (2012)
- Mashima H, Sato T, Horie Y, Nakagawa Y, Kojima I, Ohteki T, Ohnishi H.: Interferon regulatory factor-2 regulates exocytosis mechanisms mediated by SNAREs in pancreatic acinar cells. Gastroenterology 141: 1102-1113 (2011)
- Hamamoto K, Yamada S, Hara A, Kodera T, Seno M, Kojima I.: Extracellular matrix modulates insulin production during differentiation of AR42J cells: functional role of Pax6 transcription factor. J Cell Biochem 112: 318-329 (2011)
STAFF

Professor: Itaru Kojima
Associate Professor: Hiroshi Shibata
Assistant Professor: Masahiro Nagasawa
Assistant Professor: Yuko Nakagawa
Secretary: Mayumi Odagiri
Secretary: Toshiko Numata
Research Scientist: Kimitaka Kogure
Postdoctoral Fellow: Ma Jinhui
Graduate Student: Yoshiaki Ohtsu
Graduate Student: Yosuke Masubuchi
Graduate Student: Li Longfei
Research Fellow: Kunihisa Hamano
