
Reserch
Institute for Molecular and Cellular Regulation
Laboratory of Signal Transduction

Fumikazu Okajima Professor
It is said that human body consists of more than 60 trillion cells. These cells cannot be alive without their mutual communication through intercellular or extracellular signaling molecules, such as hormones, neurotransmitters, and cytokines. We are investigating their receptors and intracellular signaling mechanisms involved in the actions induced by these intercellular or extracellular signaling molecules.
Research and Education
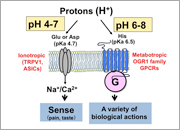
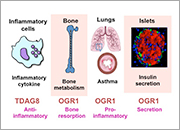
We aim to elucidate signal transduction mechanisms of lipid mediators, such as sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) and lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), and their roles in several disorders, especially atherosclerosis and cancer. We have currently developed an LPA antagonist Ki16425 and its orally active Ki16198, in collaboration with Kirin brewery Co. Ltd. This drug is potentially applicable for cancer cell invasion and metastasis, cardiovascular diseases and inflammatory diseases. We have recently found that a group of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) sense extracellular protons or pH and are coupled to the intracellular signaling pathways. As proton-sensing mechanisms, channels, such as TRPV1 and ASICs, on sensory neurons have been known as sensors for nociception and taste. On the other hand, OGR1 family GPCRs sense more physiological pH of 6 to 8 through histidine residues. They are expressed on a wide range of cell types, including neural cells. Extracellular proton concentration is around 40 nM (pH 7.4) under the physiological condition and reaches 1000 nM (pH 6.0) in tumor, ischemia, and inflammation. Thus, it is expected that these proton-sensing GPCRs mediate a variety of physiological and pathophysiological responses. We are investigating the role of proton-sensing GPCRs using knockdown cells with siRNAs and knockout mice. We have usually a few graduate students in our laboratory. They can learn the cutting edge of scientific knowledge on the related area and a variety of scientific skills required for accomplishment of experiments themselves.
 |
 |
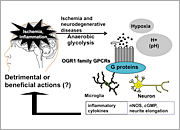 |
| Proton-sensing mechanisms in cell membranes | OGR1-family GPCRs are novel molecular targets for osteoporosis, asthma, and inflammatory disorders | Role of proton-sensing GPCRs in ischemia and neurodegenerative diseases |
Staff

Professor: Fumikazu Okajima
Associate Professor: Koichi Sato
Assistant Professor: Chihiro Mogi
Assistant Professor: Haruka Aoki
TEL: +81-27-220-8850
FAX: +81-27-220-8895
E-mail: okajima@gunma-u.ac.jp
URL: http://www.imcr.gunma-u.ac.jp/lab/sigtra/ ![]()
Recent Publication
- Aoki H, Mogi C, Hisada T, Nakakura T, Kamide Y, Ichimonji I, Tomura H, Tobo M, Sato K, Tsurumaki H, Dobashi K, Mori T, Harada A, Yamada M, Mori M, Ishizuka T, and Okajima F.: Proton-sensing ovarian cancer G protein-coupled receptor 1 on dendritic cells is required for airway responses in a murine asthma model. PLoS ONE in press (2013)
- Nakakura T, Mogi C, Tobo M, Tomura H, Sato K, Kobayashi M, Ohnishi H, Tanaka S, Wayama M, Sugiyama T, Kitamura T, Harada A, and Okajima F. Deficiency of Proton-Sensing Ovarian Cancer G Protein-Coupled Receptor 1 Attenuates Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion. Endocrinology 153:4171-4180 (2012)
- Sato K, Horiuchi Y, Jin Y, Malchinkhuu E, Komachi M, Kondo T, Okajima F.: Unmasking of LPA(1) receptor-mediated migration response to lysophosphatidic acid by interleukin-1β-induced attenuation of Rho signaling pathways in rat astrocytes. J Neurochem 117:164-174 (2011)
- Matsuzaki S, Ishizuka T, Hisada T, Aoki H, Komachi M, Ichimonji I, Utsugi M, Ono A, Koga Y, Dobashi K, Kurose H, Tomura H, Mori M, Okajima F.: Lysophosphatidic acid inhibits CCL5/RANTES production by blocking IRF-1-mediated gene transcription in human bronchial epithelial cells. J Immunol 185:4863-4872 (2010)
- Kimura T, Tomura H, Sato K, Ito M, Matsuoka I, Im DS, Kuwabara A, Mogi C, Itoh H, Kurose H, Murakami M, Okajima F.: Mechanism and role of high-density lipoprotein-induced activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 285:4387-4397 (2010)
- Malchinkhuu E, Sato K, Maehama T, Ishiuchi S, Yoshimoto Y, Mogi C, Kimura T, Kurose H, Tomura H, Okajima F: Role of Rap1B and tumor suppressor PTEN in the negative regulation of lysophosphatidic acid-induced migration by isoproterenol in glioma cells. Mol Biol Cell 20:5156-5165 (2009)
- Mogi C, Tobo M, Tomura H, Murata N, He XD, Sato K, Kimura T, Ishizuka T, Sasaki T, Sato T, Kihara Y, Ishii S, Harada A, Okajima F: Involvement of proton-sensing TDAG8 in extracellular acidification-induced inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine production in peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol 182: 3243-3251 (2009)
